The First Operations Metal Injection Molding Process
The powder Metal Injection Molding process is the blending of fine powdered materials (in this case powdered metals) and pressing these powders into a desired shape. After the desired shape has been achieved, the compressed part is heated in a controlled atmosphere, causing the material to bond.
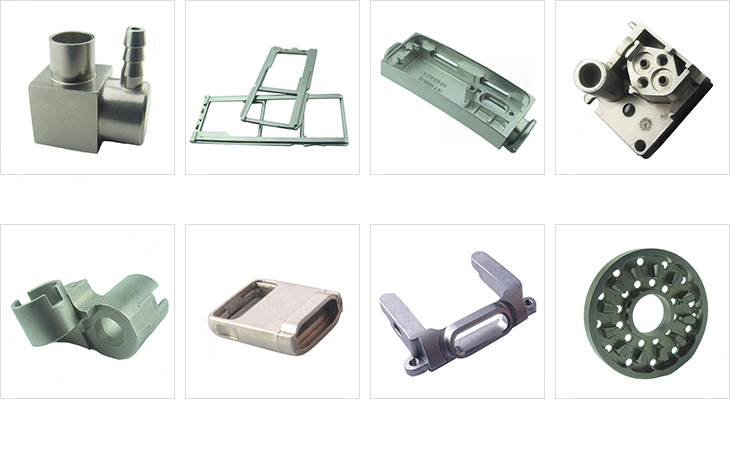

International Optimum MIM Harber's metal sintering process, also commonly known as the powder metallurgy process, is divided into three main steps:
Blending
Compaction
Sintering
Secondary Operations MIM Metal Parts
Noted here are common secondary operations used on MIM metal parts
Coining and Resizing
While most parts are nearly finished after the sintering process step, some parts do require sizing or coining operations in order to improve its structural and dimensional aspects. Sizing is able to decrease dimensional variations while coining can increase the part’s density and thus its strength. Note that some materials might need to be re-sintered after coining processes in order to re-fuse particles.
Also, coining does not occur at a fast rate, negatively impacting the cost per part.
Steam Treatment
This process is capable of increasing the sintered metal part’s resistance to corrosion, surface hardness, resistance to wear, reduces porosity, improves material density and improves the part’s surface for plating processes.
Heat Treatment
Sintered metal parts are heat treated in order to to increase the material hardness and strength, as well as increase the material’s resistance to wear.
Vacuum or Oil Impregnation
This operation makes sintered metal bearing self lubricating.
Structural Infiltration
This operation is capable of improving strength, reducing porosity and improves both ductility and machinability. Structural infiltration also seals parts so that parts are liquid and gas tight and is used to prepare the part surface for plating with other metals.
Resin or Plastic Impregnation
This operation can be used in order to improve machinability, prepare the surface of the part for plating processes and to seal the part, making it liquid or gas tight.
Machining
Machining processes here include threading, boring, milling, drilling, turning, tapping and broaching.
Grinding
Grinding on sintered metal parts includes homing, lapping and polishing.
Surface Finishing
Done in order to improve the part's surface finish, processes here includes plating, tumbling, coating, deburring and vibratory processes.

From the blending of powders through pressing, sintering, and secondary machining, our quality programs ensure production of consistent, high-quality parts. Our plants are ISO, QS, and TS 16949 certified.
You can also learn more about the advantages and disadvantages of the metal Injection Molding process.